Dense urban areas, the surge in e-commerce, high customer expectations, and vehicle maintenance are among the factors that drive last-mile costs up.

Last mile, the last stage of the delivery process, is not only time-consuming but also the costliest. According to industry reports, last-mile expenses account for approximately 53% of total delivery costs.
Understanding and cutting down these costs is essential for the success of your delivery operations. If you don't understand them, it's difficult to cut them. And if you don't take actions to reduce last mile costs, you seriously jeopardize your profits.
This article provides a clear overview of the factors driving these costs and includes useful tactics to reduce and keep them under control.
Quick Summary:
- Dense urban areas
- Failed deliveries
- Surge in e-commerce
- Package returns
- Customer expectations for speedy deliveries
- Skilled delivery workforce and labor costs
Factors contributing to last mile delivery costs
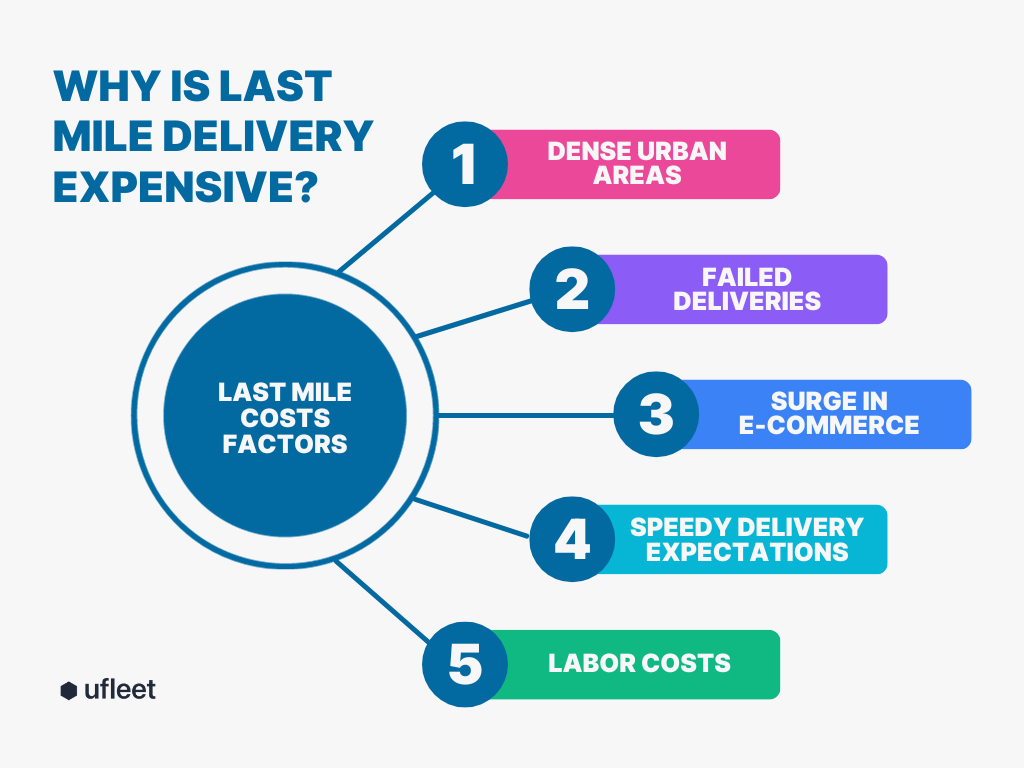
The factors for the high costs of last-mile delivery are numerous:
Dense urban areas lead to more stops and navigation challenges. The surge in e-commerce increases small-scale delivery expenses. Customer expectations for rapid deliveries add pressure for costly express options.
Maintaining a skilled delivery workforce, rising fuel prices, vehicle maintenance, and real-time tracking also contribute to the overall expenses for delivery operations.
Let’s look at each one in more detail:
Dense urban areas
As cities grow and expand, the complexity of delivery routes increases. This makes it hard for delivery drivers to efficiently reach their final destination leading to more miles driven, increased fuel consumption and plenty of idle time. In fact, In fact, the World Economic Forum found that drivers spend an average of 40% of their time idling.
Congested streets, limited parking spaces, and complicated road networks are among the challenges that last mile delivery drivers face on a daily basis. Just imagine the amount of time a driver spends looking for a parking spot in the city centre. And now imagine that they have not only one but tens of deliveries to make that day.
Fuel consumption in cities is an additional cost booster. Frequent start-stops, traffic jams, and driving at low speeds are the main reasons for the increased fuel consumption in cities.
In addition, dense urban areas lead to more scratches, dents, and bumper cracks on vehicles that require maintenance and repair.
Failed deliveries
Failed deliveries is another key contributor to last mile costs being so high. A failed delivery results both in lost sales and transportation expenses, and in most cases—an extra attempt for delivery.
It also leads to extra time in "Where is my order?" calls, going back and forth with customer to reschedule, and rearranging delivery sequences. If the failed delivery was the retailer's fault, it might also harm its reputation and result compromised brand loyalty and even permanent customer churn.
According to a study, the cost for a failed delivery is an average of $17.20 per order in the US, £11.60 in the UK and €14.60 in Germany. The average yearly cost was $193,730 in the US, £68,084 in the UK and €144,354 in Germany. The average failed delivery rate in these countries was between 6% and 8%.
The most common factors leading to failed deliveries:
- Nobody was at the address
- Incorrect or incomplete address
- Incorrect or incomplete contact details
- Poor communication between dispatchers and drivers
- Poor delivery route optimization that messes up delivery windows
- Damaged or wrong package
- External factors like traffic jams, road closures, accidents, etc
Retailers can prevent most of these situations by implementing a route optimization software (more on this in the next section).
Surge in e-commerce
The rapid growth of online shopping leads to a huge increase in the number of small-scale deliveries to individual households. And more orders means more deliveries, hence more costs.
According to Statista, the total e-commerce revenue is expected to reach US$4,117.00bn in 2024. The estimated annual growth rate (CAGR 2024-2029) is 9.49%, which is said to result in market volume of US$6,478.00bn by 2029.
Some of the main reasons for the surge in e-commerce include the ever-evolving online shopping experience, the social e-commerce trend, the increasing number of internet users, the GDP growth, and even the impact of artificial intelligence.
Package returns
Most customers return packages because of poor product quality, size and fit issues, buyer's change of mind, no longer needing the product, found a better price elsewhere, etc.
Returns and refunds are another factor that makes the last-mile process expensive. They have a significant financial and operational impact on businesses. Returns and refunds reduce profit margins due to restocking and shipping costs and operationally they require extra resources for handling and processing.
According to a study, returns costed retailers $761 billion globally in 2023. In the US alone, they led to $816 billion in lost sales annually. We're about to see what that data will show for 2024 but it will most probably be more.
Customer expectations for speedy deliveries
Customer expectations for same-day or next-day delivery are rising. According to various reports, 90% of customers demand same-day or next-day service.
In 2023, 86% of respondents defined “fast delivery” as delivery within two days or less, and 58% paid more for a faster than the usual delivery.
Faster delivery times require expedited shipping methods, dedicated delivery resources, and extended operating hours, which incur higher expenses.
Skilled delivery workforce and labor costs
A skilled and reliable delivery workforce is essential for timely and efficient last-mile deliveries.
Drivers can make or break the delivery process and play a key role in maintaining brand reputation.
If they are not doing their job well, customers will complain. However, skilled drivers are difficult to find as competition for qualified personnel is enormous.
That's why businesses need to invest in attractive compensation, growth opportunities, and work culture. This requires a budget.
How to reduce last mile delivery costs
Innovative technologies and targeted tactics allow businesses to identify cost-saving opportunities.
Ultimately, this leads to enhancing their bottom line and maintaining a competitive edge in the ever-evolving delivery business.
Let’s look at some tactics to reduce last-mile costs.
Route optimization software
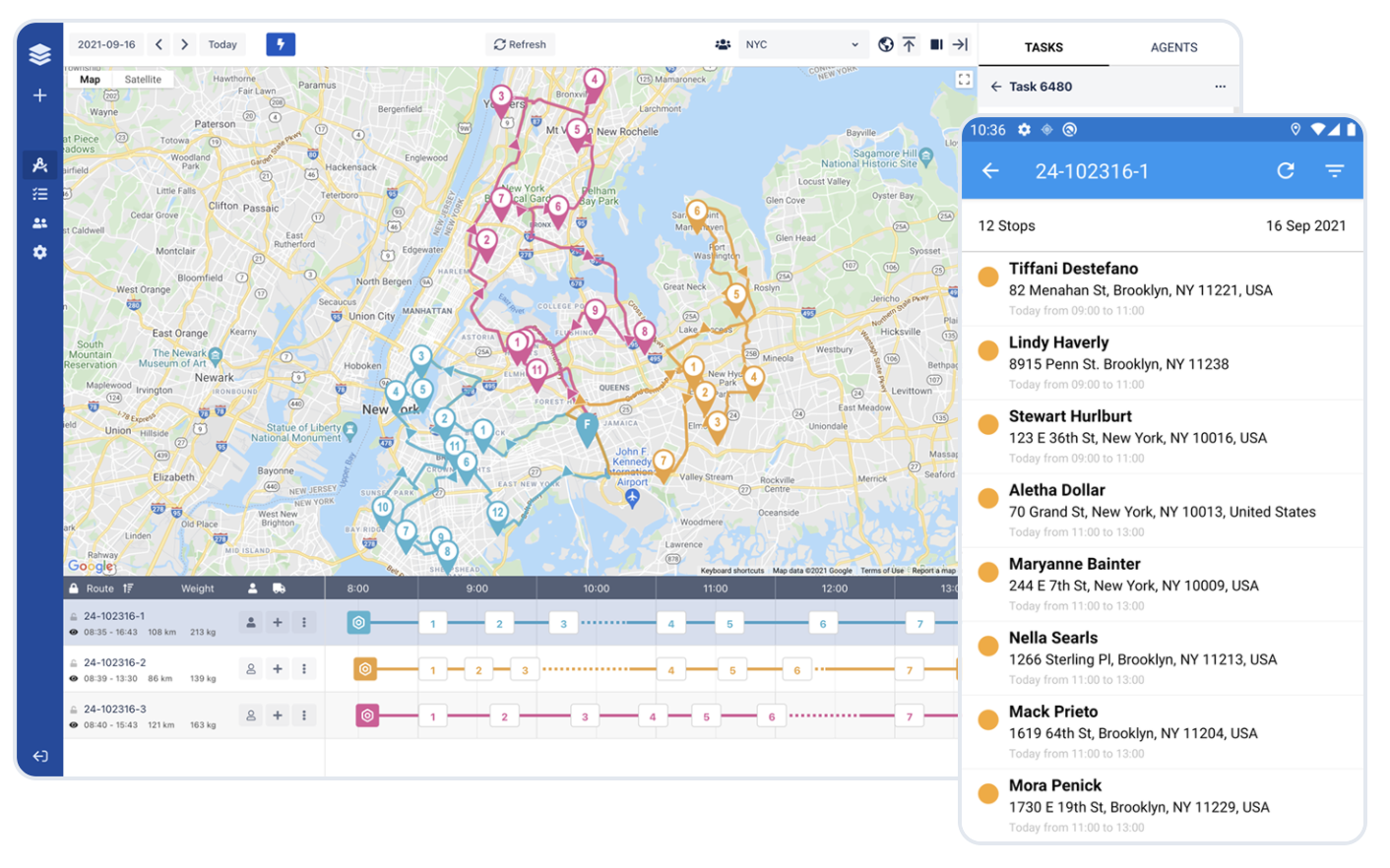
Route planning software or delivery management software is a robust technology that significantly reduces the costs associated with delivery.
Such platforms offer numerous functionalities:
- Delivery route optimization and planning
- Real-time communication between customers, drivers, and dispatchers
- Real-time delivery tracking
- Proof of delivery
- Feedback on delivery
- Reports and analytics
Delivery management platforms use intelligent AI algorithms to pick the best routes. They take into account delivery windows, delivery sequencing, and the number of deliveries per day.
They also help dispatchers, delivery drivers, and customers to communicate in real-time through mobile apps.
Additionally, reports and analytics provide insights into delivery performance, helping businesses identify pitfalls and optimize resources.
This results in various benefits:
- Less total mileage and fuel consumption
- Optimized schedules for multiple deliveries
- Fewer missed or failed deliveries
- Better experience for the customer and staff members
- Businesses get better insights into their delivery process
At Ufleet we can help you solve each one of these challenges. We also created this cost optimization calculator to help you how much you can save by using the platform.
Micro-fulfillment centers
Micro-fulfillment centers are smaller-scale distribution facilities strategically placed closer to densely populated urban areas or customer clusters.
This reduces last-mile distance and results in faster and more efficient deliveries.
The approach is particularly beneficial in dense urban environments. The reason is it decreases travel time, hence fuel consumption and working hours for drivers.
Businesses should plan such centers carefully, though. Additional facilities come with extra costs for rent, utilities, and staffing.
To make sure they will reduce total costs rather than increase them, businesses should do their math before investing in them.
Diversify delivery options
Providing flexible delivery options empowers customers to choose a method that best fits their convenience. Click-and-collect, locker delivery, and parcel shops offer alternatives to traditional home deliveries.
This reduces the need for separate delivery attempts, leading to cost savings and increased delivery efficiency. These diverse delivery choices cater to varying preferences, ensuring customer satisfaction while optimizing last-mile operations for businesses.
Delivery companies can use alternative delivery methods. This includes bicycles, or electric vehicles to reduce last-mile delivery costs. In addition, these methods are environmentally friendly.
Autonomous delivery
Companies like Nuro, Starship Technologies, and Serve Robotics lead the rise of autonomous delivery.
Imagine containers (of various sizes) on wheels. Once a human loads and configures them for a particular destination, they can move on their own from point A to point B.
Autonomous delivery robots rely on cameras for 360-degree vision, ultrasonic sensors, GPS navigation, measurement units, gyroscopes, and more to navigate throughout the city.
They produce zero carbon emissions and can easily navigate traffic congestion because of their smaller size.
Yes, it’s a costly initial investment but pays off in the long run.
Looking forward, autonomous delivery stands as a strategic solution for cost-effective and sustainable delivery operations.
Autonomous delivery robots will play role in multimodal delivery in the future
Takeaways
Here are the most important highlights from this article:
Challenges:
- Last-mile expenses account for approximately 53% of total delivery costs.
- Dense urban areas increase fuel consumption and idle time.
- Failed deliveries lead to lost sales and transportation costs.
- E-commerce leads to more individual orders and high costs for returns and refunds.
- Retailers need more resources to meet customer expectations for speedy delivery.
Solutions:
- Micro-fulfillment centers are a strategic move to serve more locations and find efficient routes.
- Alternative delivery options such as click-and-collect or locker delivery can reduce delivery costs.
- Route optimization software leads to less fuel consumption, fewer failed deliveries, and increased customer satisfaction.
- Autonomous delivery vehicles offer cost-efficient and eco-friendly delivery.
If you enjoyed this article, subscribe below and you’ll get more like this each month.
.
Never miss a post
You may also like…
You too can reduce costs and improve efficiency with Ufleet
- plan and optimize delivery routes
- manage and empower drivers
- enhance customer experience
- make data-driven business decisions
We’d love to learn about your challenges.
Leave your email and we’ll get back to you.